Traditional farming
Years: 1960
World population: 3 billion
Key Aspects
Negative:
- Low crop productivity
- Coexistence with different pests
Positive:
- Foods with greater flavor and aroma (organoleptic properties).
- No residue.
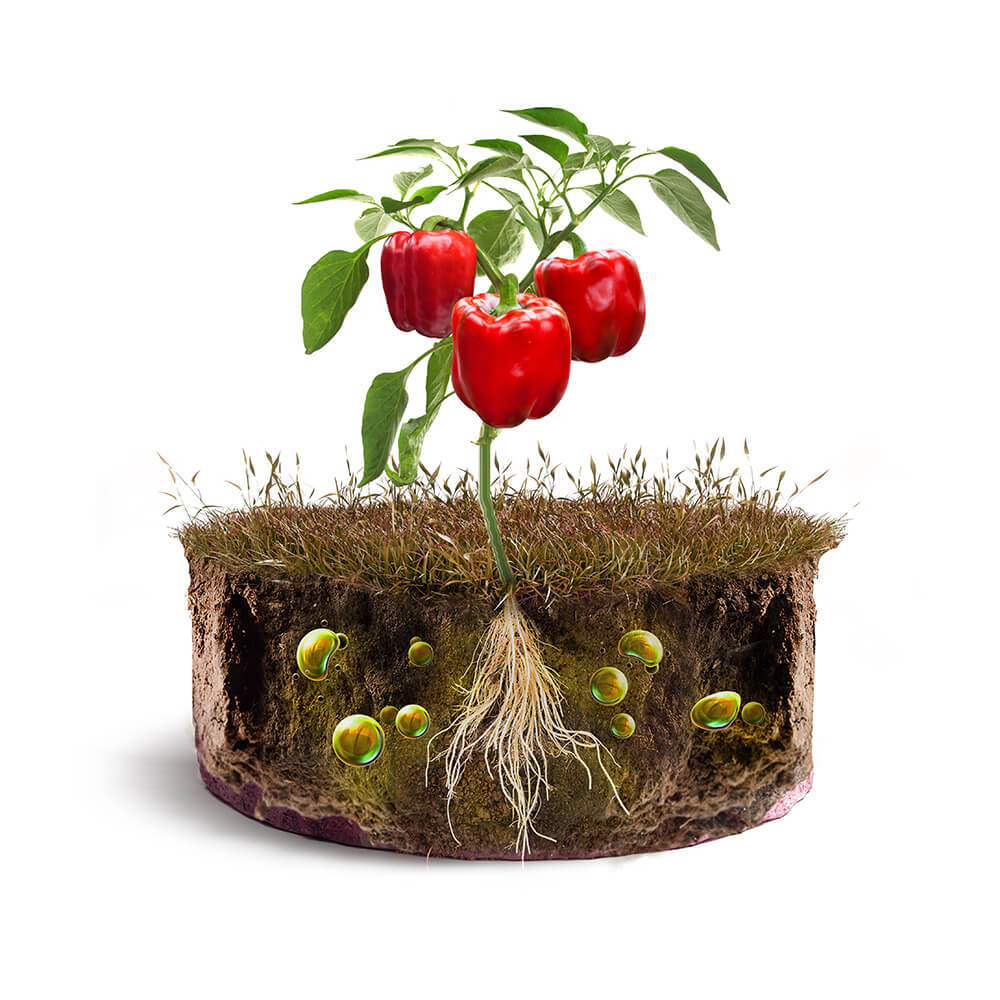

Industrial farming
Years: 1960 – 2017
World population: 5,2 billion
Changes compared to industrial agriculture:
- Widespread application of chemical pesticides
- Soil disinfection.
Key Aspects
Negative:
- Less flavor/aroma.
- Massive appearance of residues in food.
- Pollution.
Positive:
- Increase the yield.
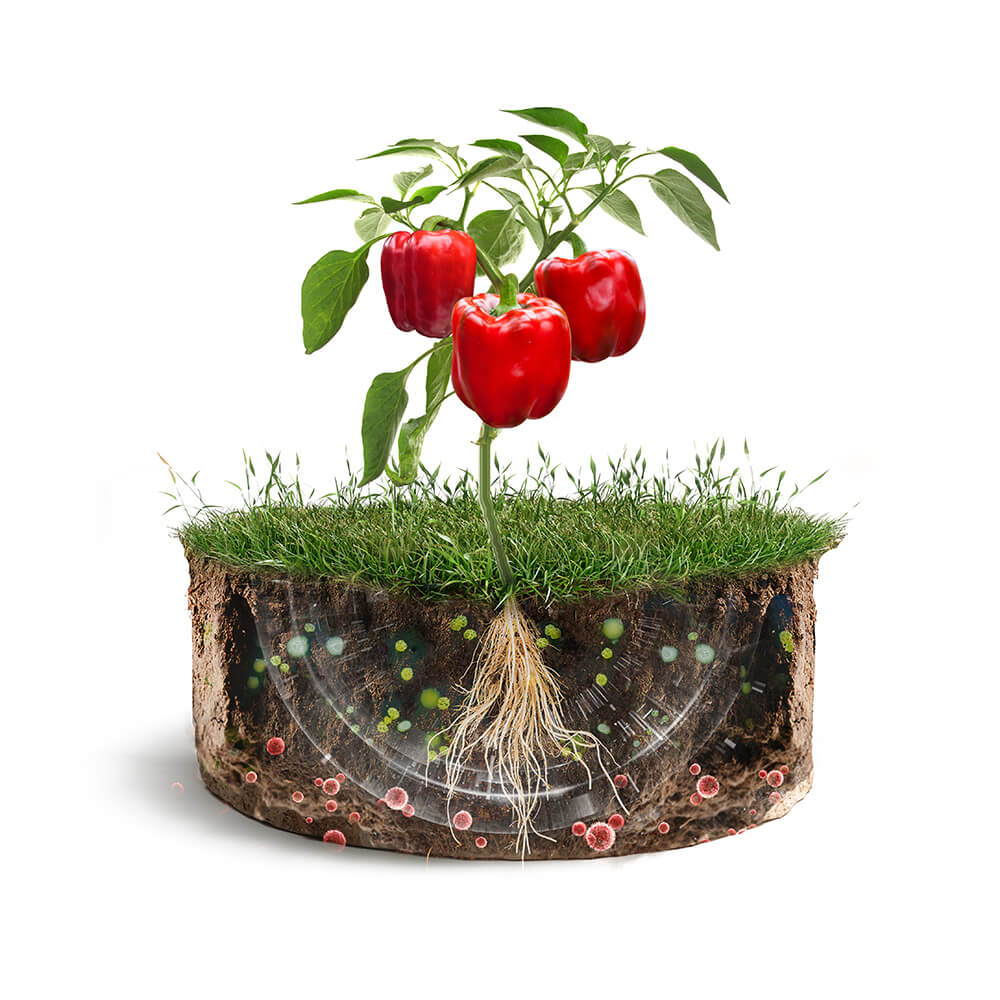

Agrobiotic Movement
Years: 2017 – ….
World population: +7.5 billion
Changes compared to industrial agriculture:
- Use of biopesticides.
- Inoculation of soil with probiotics and prebiotics.
Key Aspects
Negative: no negative effect.
Positive:
- Barrier effect due to colonization.
- Equal productivity.
- Greater flavor and aroma (organoleptic properties) and chemopreventive action.
- Zero residues.
- Rational management of water and fertilizers
It does not pollute the environment.

The soil is home to most of the living biomass on our planet.
Welcome to the new agriculture, welcome to the Agrobiotic Movement
Notice: Undefined index: video in /var/www/vhosts/kimitecagro.com/httpdocs/wp-content/plugins/kimitec-group/page-movimiento.php on line 48
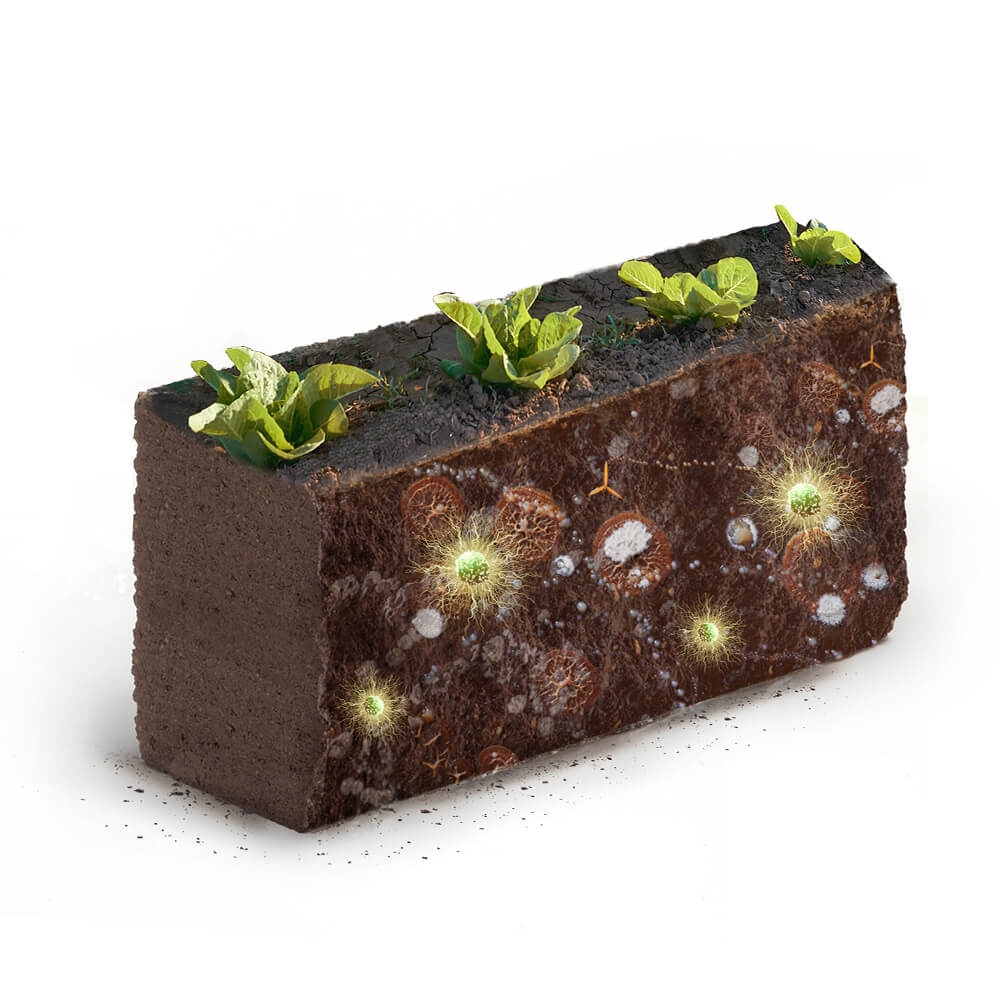
Prebiotics
Prebiotics are compounds or active biomolecules that act as food for beneficial microorganisms (probiotics), enhancing their activity, increasing their concentration in the soil and thus, indirectly contributing to the production of crops with higher yields and quality. Depending on the composition of prebiotics, they can be selective in feeding the microorganisms to promote their growth and action in the soil at specific times.

Notice: Undefined index: video in /var/www/vhosts/kimitecagro.com/httpdocs/wp-content/plugins/kimitec-group/page-movimiento.php on line 40
Probiotics
Microorganisms involved in the dynamics and quality of the rhizosphere and soil microbiota, influencing crop development. The use of probiotics promotes the adaptation of crops in unfavorable conditions, improvinge organoleptic characteristics (flavor and aroma), optimizing the absorption of nutrients, increasing yield, increasin the nutritional content of foods, strengthening the plant, and even competing for the ecological niche against pathogenic microorganisms.
Part of the microorganisms that constitute the living part of the floor, we can find beneficial fungi such as Mycorrhizae, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria, pseudomonas producers of siderophores, consortia of rhizobacteria that promote the overall development of the crop, etc.
Benefits of the Agrobiotic Movement
- Recovery of flavor and aromas.
- More quality and uniformity in the harvests.
- Restoration of the microbiological balance.
- More fertile and productive soils.

- Increases functional properties of food.
- Enhances the chemopreventive action of food.
- Positive repopulation of disinfected soils.
- Greater crop yield.
.png)
.png)